However, it doesn't take much time to understand the specifics of the pixelated world. Download minecraft full version for free on mac. As the night approaches, your character needs to use an inventory of items and skins to defeat the mobs of monsters.
On your Mac, select an item, then choose File Get Info. Click the lock icon to unlock it. Enter an administrator name and password. In the Sharing & Permissions section, do any of the following: Add a user or group: Click the Add button below the list, select a user or group, then click Select. Remove a user or group: Select the user or group, then click the Remove button below the list. Run chmod u+x /Desktop/myCommandScript.command in your terminal, where /Desktop/myCommandScript.command is the path to your script.
Script File For Mac Shortcut
Basically, a Mac application has a .app extension, but it's not really a file — it's a package. You can view the application's contents by navigating to it in the Finder, right-clicking it and then choosing 'Show Package Contents'.
The internal folder structure may vary between apps, but you can be sure that every Mac app will have a Contents folder with a MacOS subfolder in it. Inside the MacOS directory, there's an extension-less file with the exact same name as the app itself. This file can be anything really, but in its simplest form it's a shell script. As it turns out, this folder/file structure is all it takes to create a functional app!
Run Script On Mac
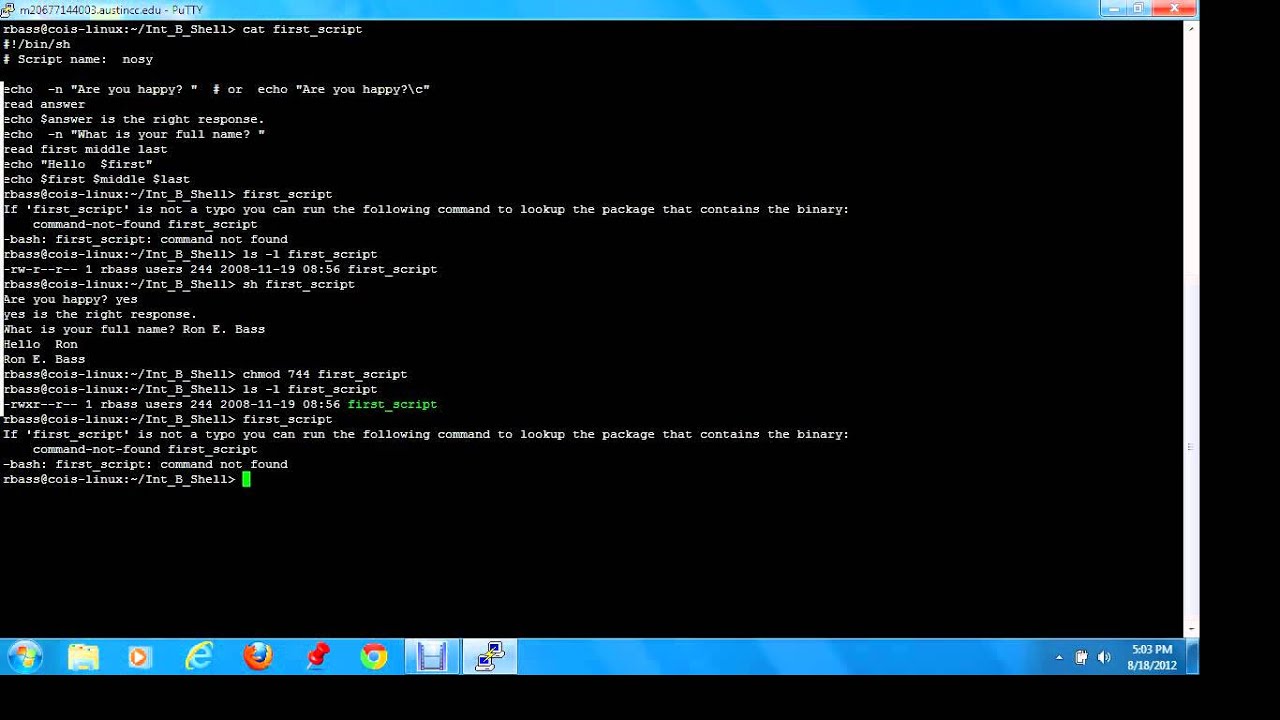
Script files are launched from an application's script menu or from the Mac OS system-wide Script Menu utility. Script applications, or 'applets,' are launched like other applications by double-clicking their icons in the Finder or by clicking their Dock or Finder Toolbar and Sidebar icons. You can also execute a script from a file by running perl interpreter as the command and giving the script as a parameter (in this case execute permissions to the script are not needed): perl /path/to/script/script1.pl. Shell scripts must be executable files in order to run. You can use the chmod command to indicate that the text file is executable (that is, its contents can be run as a shell script). In the Terminal app on your Mac, use the cd command to move into the directory that contains the file you want to make executable.
Enter appify
After this discovery, Thomas Aylott came up with a clever 'appify' script that allows you to easily create Mac apps from shell scripts. The code looks like this:
Installing and using appify is pretty straightforward if you're used to working with UNIX. (I'm not, so I had to figure this out.) Here's how to install it:
- Save the script to a directory in your
PATHand name itappify(no extension). I chose to put it in/usr/local/bin, which requires root privileges. - Fire up Terminal.app and enter
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/appifyto make appify executable without root privileges.
After that, you can create apps based on any shell script simply by launching Terminal.app and entering something like this:
This audio editing software is a full-featured professional audio and music editor for Windows and Mac. Record and edit music, voice and other audio recordings. When editing audio files, you can cut, copy and paste parts of recordings, and then add effects like echo, amplification and noise reduction. WavePad works as a WAV or MP3 editor, but it also supports a number of other file formats. Free music editor for mac. Music Tag Editor for Mac is a convenient program for helping you keep all your music organized. It works smoothly, and the variety of features it offers means that you can see all of your music.
Obviously, this would create a stand-alone application named Your App Name.app that executes the your-shell-script.sh script.
After that, you can very easily add a custom icon to the app if you want to.
Adding a custom app icon
- Create an
.icnsfile or a 512×512 PNG image with the icon you want, and copy it to the clipboard (⌘ + C). (Alternatively, copy it from an existing app as described in steps 2 and 3.) - Right-click the
.appfile of which you want to change the icon and select 'Get Info' (or select the file and press ⌘ + I). - Select the app icon in the top left corner by clicking it once. It will get a subtle blue outline if you did it right.
- Now hit ⌘ + V (paste) to overwrite the default icon with the new one.
Note that this will work for any file or folder, not just .app files.
Examples

Chrome/Chromium bootstrappers
I like to run Chrome/Chromium with some command-line switches or flags enabled. On Windows, you can create a shortcut and set the parameters you want in its properties; on a Mac, you'll need to launch it from the command line every time. Well, not anymore :)
Bash Script Mac
The & at the end is not a typo; it is there to make sure Chromium is launched in a separate thread. Without the &, Chromium would exit as soon as you quit Terminal.app.
Launch a local web server from a directory
Say you're working on a project and you want to debug it from a web server. The following shell script will use Python to launch a local web server from a specific directory and open the index page in your default browser of choice. After appifying it, you won't even need to open the terminal for it anymore.
Obviously, this would create a stand-alone application named Your App Name.app that executes the your-shell-script.sh script.
After that, you can very easily add a custom icon to the app if you want to.
Adding a custom app icon
- Create an
.icnsfile or a 512×512 PNG image with the icon you want, and copy it to the clipboard (⌘ + C). (Alternatively, copy it from an existing app as described in steps 2 and 3.) - Right-click the
.appfile of which you want to change the icon and select 'Get Info' (or select the file and press ⌘ + I). - Select the app icon in the top left corner by clicking it once. It will get a subtle blue outline if you did it right.
- Now hit ⌘ + V (paste) to overwrite the default icon with the new one.
Note that this will work for any file or folder, not just .app files.
Examples
Chrome/Chromium bootstrappers
I like to run Chrome/Chromium with some command-line switches or flags enabled. On Windows, you can create a shortcut and set the parameters you want in its properties; on a Mac, you'll need to launch it from the command line every time. Well, not anymore :)
Bash Script Mac
The & at the end is not a typo; it is there to make sure Chromium is launched in a separate thread. Without the &, Chromium would exit as soon as you quit Terminal.app.
Launch a local web server from a directory
Say you're working on a project and you want to debug it from a web server. The following shell script will use Python to launch a local web server from a specific directory and open the index page in your default browser of choice. After appifying it, you won't even need to open the terminal for it anymore.
Mac Os Shell Script
More?
Script File Format
Needless to say, the possibilities are endless. Just to give another example, you could very easily create an app that minifies all JavaScript and CSS files in a specific folder. Got any nice ideas? Let me know by leaving a comment!
